Measuring Weighing Quality - Understanding Accuracy and Standard Deviation for Operational Excellence


Reading time: 5 minutes
In the world of weighing, measuring accuracy is critical for ensuring product quality, operational efficiency, and ultimately, profitability. When we talk about “accuracy” in weighing, we're not simply referring to a single perfect number but rather a reliable performance within acceptable tolerances. To understand this better, we need to differentiate between two critical concepts: accuracy and standard deviation.
Understanding these factors can illuminate where improvements in weighing technology or practices can lead to substantial operational gains, especially when you operate in a business with expensive products. As I often explain to my customers: “Measuring weighing quality accurately is not just about precision but about how repeatable and reliable the results are — which in turn can mean the difference between net profit or loss.”
In this blog, we’ll explore how accuracy, standard deviation, and statistical measures like 1-sigma and 2-sigma (σ) levels influence weighing outcomes and how improvements here can drive rapid returns on investment.
What is accuracy in weighing?
Accuracy in weighing is often defined as the degree of closeness between the actual weight of a product and the measured weight displayed by the weighing system. Accurate measurements mean that a scale consistently provides values close to the true weight of the material being measured. However, precision alone is not the only measure of quality.
Achieving high accuracy in weighing can be challenging due to environmental factors like vibrations, air currents, and even temperature changes that can affect the outcome. This is where we start to see the importance of repeatability, or consistency in measurement, which brings us to the concept of standard deviation.
Standard deviation: Why consistency matters!
Standard deviation, represented by the Greek letter sigma (σ), is a statistical measure that reflects the variability or dispersion in a set of values. In weighing systems, standard deviation tells us how consistently a scale can reproduce the same measurement across multiple trials.
Let’s break it down further:
- Sigma (1σ): This represents a measurement that is within one standard deviation of the mean or average value. In weighing, this means the majority of measurements will fall within a certain range of the actual weight are about 65%.
- 2-Sigma (2σ): Measurements within two standard deviations cover an even broader range, encompassing about 95% of measurements around the mean. This level of consistency is often a key quality target in industrial settings, providing a balance between accuracy and operational efficiency.
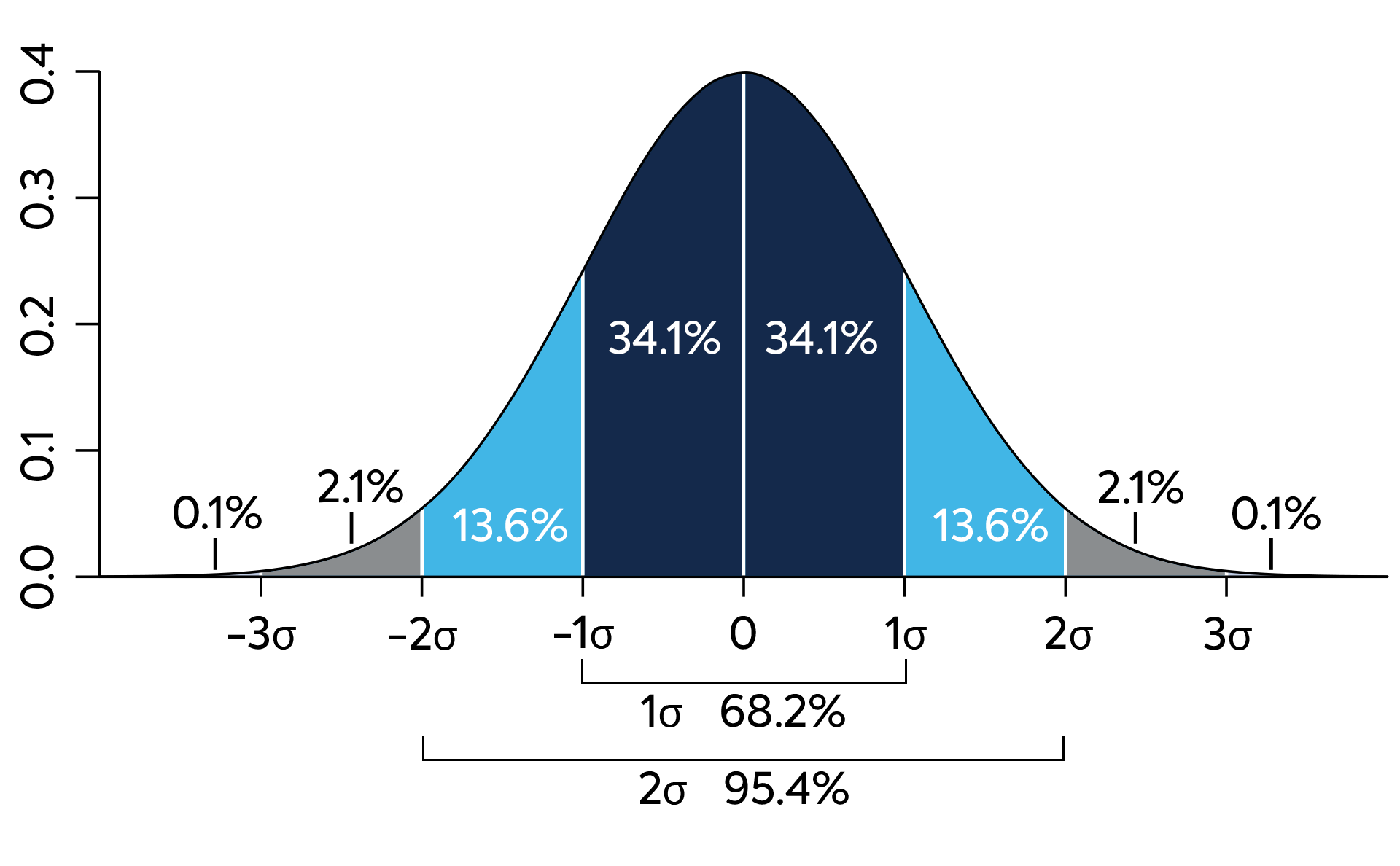
“Ensuring that a weighing system can consistently achieve 1σ or 2σ levels means you can have confidence that the majority of measurements are accurate and reliable. This consistency directly affects your amount of product give-away and profit margin — which for many manufacturers can mean an extremely rapid return on investment.”
Accuracy vs. standard deviation: Why both matter?
In practical terms, accuracy and standard deviation must be balanced to achieve optimal weighing quality. An accurate system may yield one correct measurement, but if it cannot replicate that accuracy repeatedly, it introduces variability. This inconsistency can lead to batch rejections, increased product give-away, or customer dissatisfaction, and all will impact profitability.
To put this into perspective:
- High accuracy, low standard deviation: This is the ideal scenario where the scale is both accurate and consistent. It ensures that products meet specifications with minimal variation.
- High accuracy, high standard deviation: Here, the system is accurate on average but inconsistent in individual measurements. This can lead to significant rework costs and product quality issues.
- Low accuracy, low standard deviation: Consistently inaccurate results lead to systematic errors, often necessitating recalibration or equipment replacement.
- Low accuracy, high standard deviation: Inconsistent and inaccurate results indicate severe issues with the weighing process, rendering the data unreliable.
Achieving the right balance is more than just quality assurance; it is about generating tangible financial impact.
“Every percentage point of accuracy improvement translates directly to fewer errors, less product give-away, and a stronger bottom line. It is why investing in better weighing / bagging systems provides rapid returns.”
Measuring ROI through improved weighing quality
The financial returns from investing in accurate and consistent weighing systems can be substantial. A high-quality weighing system minimizes product give-away (delivering more than required), rejects (not meeting weight standards), and the need for rework. These savings are immediate and significant, especially in industries like food, feed, pharma and chemical manufacturing; where more expensive products are handled, precision is paramount.
“Investing in weighing technology that meets high standards of accuracy and low standard deviation is not just an expense — it’s a profit-driving move. By reducing variability and improving accuracy, companies see an incredibly rapid return on investment, often within the first year of implementation.”
Ready to get started with an automated bagging solution?
Whether you want to increase production capacity, improve working conditions, or upgrade older units, Premier Tech is ready to respond with a bagging machine that suits your needs.